Surgical Excision on Recurrent Furunculosis with Plasmacytosis: a Case Report
Downloads
Introduction : Furunculosis is a skin inflammation of hair follicle which may become chronic and recurrence. Plasmacytosis is a rare lymphoproliferative disorder involving skin and systemic organs. Here in we report a case of reccurent furunculosis with plasmacytosis treated with surgical excision.
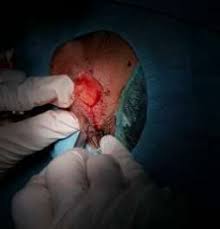
Case : A 57-years-old woman presented to our outpatient clinic with a recurrent lumps filled with pus on her left cheek since 2 years ago. Dermatological examination obtained a solitary nodule on the erythematous base skin filled with pus. Laboratory findings did not indicate the monoclonality of electrophoretic serum protein. Histopathological features of skin biopsy showed inflammatory cells aggregate in the perifollicular area consisting neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and plasma cells mainly in the dermal layer. The CD 138 immunostaining was positive, hence we diagnosed the patient with recurrent furunculosis with plasmacytosis. Surgical excision was conducted and no recurrence has been reported since then.
Discussion : Chronic and recurrent furunculosis leads to plasma reactivity against inflammation, promoting plasma cell deposition as the risk of cutaneous plasmacytosis. Histopathological examination and immunostaining may helpful to establish the diagnosis of plasmacytosis occuring in chronic skin infections. Surgical intervention can be performed on furunculosis cases with fluctuated and solitary lesion resulting in less recurrence.
Copyright (c) 2022 Alfina Rahma, Prasetyadi Mawardi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.











